Observation |
Definition |
A observation is a statistical unit on which are carried out a serie of measures |
A classical data set in statistics is a table where each line represents an observation and each row represent the same measure carried out on all the observations |
It can be useful sometimes to consider a group of observations as a single observation, in this case the measures carried out are agregated measures on the group of observations (percentage, mean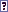 , sum, minimal value, maximal value, etc...) , sum, minimal value, maximal value, etc...) |
Example 1 |
| |
|
variable 1 |
variable 2 |
variable 3 |
variable 4 |
| |
name |
gender |
age |
height |
weight |
| observation 1 |
Aubrey |
M |
41 |
74 |
170 |
| observation 2 |
Ron |
M |
42 |
68 |
166 |
| observation 3 |
Carl |
M |
32 |
70 |
155 |
| observation 4 |
Antonio |
M |
39 |
72 |
167 |
| observation 5 |
Deborah |
F |
30 |
66 |
124 |
| observation 6 |
Jacqueline |
F |
33 |
66 |
115 |
| observation 7 |
Helen |
F |
26 |
64 |
121 |
| observation 8 |
David |
M |
30 |
71 |
158 |
| observation 9 |
James |
M |
53 |
72 |
175 |
| observation 10 |
Michael |
M |
32 |
69 |
143 |
| observation 11 |
Ruth |
F |
47 |
69 |
139 |
| observation 12 |
Joel |
M |
34 |
72 |
163 |
| observation 13 |
Donna |
F |
23 |
62 |
98 |
| observation 14 |
Roger |
M |
36 |
75 |
160 |
| observation 15 |
Yao |
23 |
M |
70 |
145 |
| observation 16 |
Elizabeth |
F |
31 |
67 |
135 |
| observation 17 |
Tim |
M |
29 |
71 |
176 |
| observation 18 |
Susan |
F |
28 |
65 |
131 |
|
Example 2 |
Example of group observations considered as single observations |
The data are per capita numbers of cigarettes smoked (sold) by 43 states and the District of Columbia in 1960 together with death rates per thouusand population from
various forms of cancer. |
Number of cases: 44 |
Variable Names: |
CIG = Number of cigarettes smoked (hds per capita) |
BLAD = Deaths per 100 population from bladder cancer |
LUNG = Deathes per 100 population from lung cancer |
KID = Deaths per 100 population from bladder cancer |
LEUK = Deaths per 100 population from leukemia |
| |
| STATE |
CIG |
BLAD |
LUNG |
KID |
LEUK |
| AL |
18.20 |
2.90 |
17.05 |
1.59 |
6.15 |
| AZ |
25.82 |
3.52 |
19.80 |
2.75 |
6.61 |
| AR |
18.24 |
2.99 |
15.98 |
2.02 |
6.94 |
| CA |
28.60 |
4.46 |
22.07 |
2.66 |
7.06 |
| CT |
31.10 |
5.11 |
22.83 |
3.35 |
7.20 |
| DE |
33.60 |
4.78 |
24.55 |
3.36 |
6.45 |
| DC |
40.46 |
5.60 |
27.27 |
3.13 |
7.08 |
| FL |
28.27 |
4.46 |
23.57 |
2.41 |
6.07 |
| ID |
20.10 |
3.08 |
13.58 |
2.46 |
6.62 |
| IL |
27.91 |
4.75 |
22.80 |
2.95 |
7.27 |
| IN |
26.18 |
4.09 |
20.30 |
2.81 |
7.00 |
| IO |
22.12 |
4.23 |
16.59 |
2.90 |
7.69 |
| KS |
21.84 |
2.91 |
16.84 |
2.88 |
7.42 |
| KY |
23.44 |
2.86 |
17.71 |
2.13 |
6.41 |
| LA |
21.58 |
4.65 |
25.45 |
2.30 |
6.71 |
| ME |
28.92 |
4.79 |
20.94 |
3.22 |
6.24 |
| MD |
25.91 |
5.21 |
26.48 |
2.85 |
6.81 |
| MA |
26.92 |
4.69 |
22.04 |
3.03 |
6.89 |
| MI |
24.96 |
5.27 |
22.72 |
2.97 |
6.91 |
| MN |
22.06 |
3.72 |
14.20 |
3.54 |
8.28 |
| MS |
16.08 |
3.06 |
15.60 |
1.77 |
6.08 |
| MO |
27.56 |
4.04 |
20.98 |
2.55 |
6.82 |
| MT |
23.75 |
3.95 |
19.50 |
3.43 |
6.90 |
| NB |
23.32 |
3.72 |
16.70 |
2.92 |
7.80 |
| NE |
42.40 |
6.54 |
23.03 |
2.85 |
6.67 |
| NJ |
28.64 |
5.98 |
25.95 |
3.12 |
7.12 |
| NM |
21.16 |
2.90 |
14.59 |
2.52 |
5.95 |
| NY |
29.14 |
5.30 |
25.02 |
3.10 |
7.23 |
| ND |
19.96 |
2.89 |
12.12 |
3.62 |
6.99 |
| OH |
26.38 |
4.47 |
21.89 |
2.95 |
7.38 |
| OK |
23.44 |
2.93 |
19.45 |
2.45 |
7.46 |
| PE |
23.78 |
4.89 |
12.11 |
2.75 |
6.83 |
| RI |
29.18 |
4.99 |
23.68 |
2.84 |
6.35 |
| SC |
18.06 |
3.25 |
17.45 |
2.05 |
5.82 |
| SD |
20.94 |
3.64 |
14.11 |
3.11 |
8.15 |
| TE |
20.08 |
2.94 |
17.60 |
2.18 |
6.59 |
| TX |
22.57 |
3.21 |
20.74 |
2.69 |
7.02 |
| UT |
14.00 |
3.31 |
12.01 |
2.20 |
6.71 |
| VT |
25.89 |
4.63 |
21.22 |
3.17 |
6.56 |
| WA |
21.17 |
4.04 |
20.34 |
2.78 |
7.48 |
| WI |
21.25 |
5.14 |
20.55 |
2.34 |
6.73 |
| WV |
22.86 |
4.78 |
15.53 |
3.28 |
7.38 |
| WY |
28.04 |
3.20 |
15.92 |
2.66 |
5.78 |
| AK |
30.34 |
3.46 |
25.88 |
4.32 |
4.90 |
|
| |
| Data from J.F. Fraumeni, "Cigarette Smoking and Cancers of the Urinary Tract: Geographic Variations in the United States," Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 41, 1205-1211. |

